Streaming 102: The world beyond batch
- tags: Bigdata,Flink,Dataflow Model,Streaming
- source: “Streaming 102: The World beyond Batch – O’Reilly.” Accessed January 5, 2022. https://www.oreilly.com/radar/the-world-beyond-batch-streaming-102/.
Three more concepts:
- Watermarks: Useful for event time windowing. All input data with event times less than watermark have been observed.
- Triggers: Signal for a window to produce output.
- Accumulation: The way to handle multiple results that are observed for the same window.
Streaming 101 Redux⌗
What: Transformations⌗
Where: windowing⌗
Make a temporal boundary for a unbounded data source.
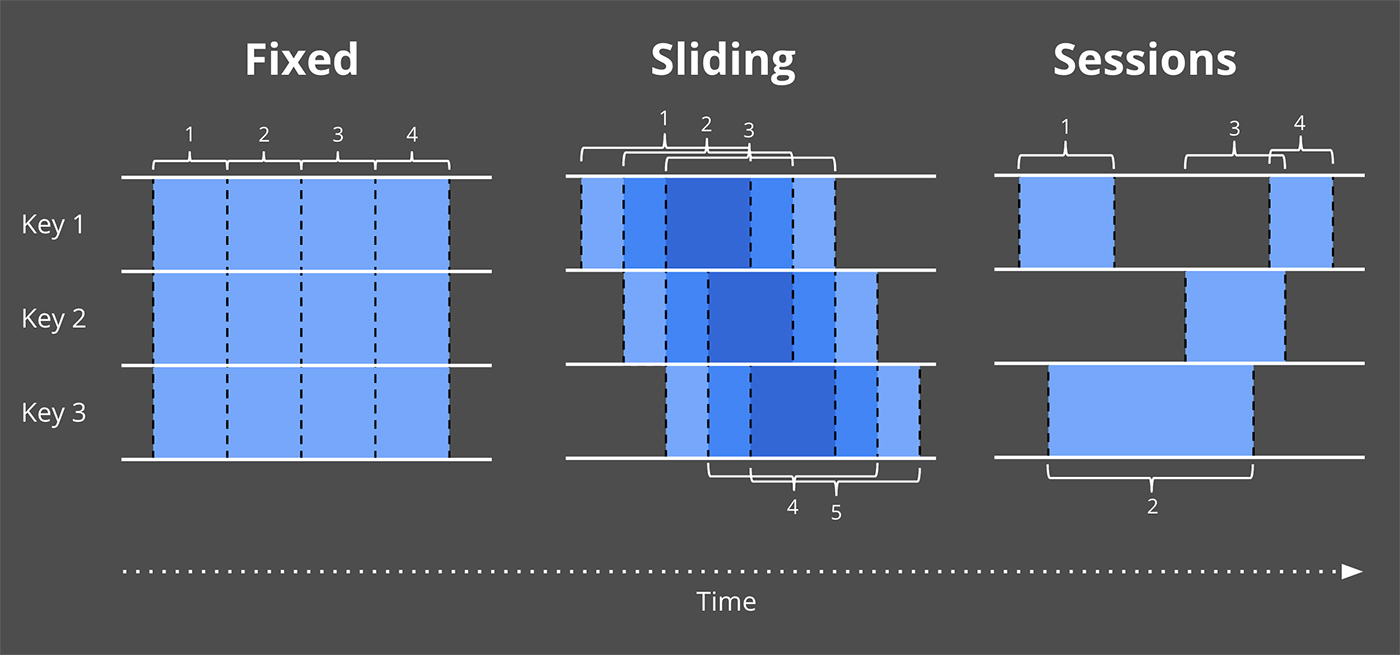
- Fixed window
- Sliding window
- Session window
Streaming 102⌗
When: watermarks⌗
Watermarks is a function: \(F(P) -> E\)
- P - processing time
- E - event time, all inputs with event time less than E have been observed.
The guarantee of watermarks:
- Perfect watermarks: no late data, all inputs with event time less than watermarks have been observed.
- Heuristic watermarks: may have late data, as accurate as possible. The data may late if the gap between processing time and event time is too large.
When: windows are materialized? The watermark passes the end of the window.
Shortcomings of watermarks:
- Too slow: will be very slow to konwn unprocessed data.
- Too fast: window may miss data that cause late data.
When: triggers⌗
Triggers complete watermarks that answered: When in processing time are results materialized?
Triggers:
- Watermark progress: implicit version that will be trigger when the watermark passed the end of the window.
- Processing time progress
- Element counts: Triggering when some finite number of elements have been observed in a window.
- Punctuations: data-dependent triggers
Composite triggers:
- Repetitions
- Conjunctions (logical AND)
- Disjunctions (logical OR)
- Sequences
How: accumulation⌗
Do refinements of results relate when multiple panes are produced by triggers in a single window.
Three different modes of accumulation:
- Discarding
- Accumulating
- Accumulatin & retracting
Where: session windows⌗
Captures a period of activity, terminated by a gap of inactivity.
Intermezzo⌗
- What results are calculated? Answered via transformations.
- Where in event time are results calculated? Answered via windowing.
- When in processing time are results materialized? Answered via watermarks and triggers.
- How do refinements of results relate? Answered via accumulation modes.